DEVELOPING A NETWORK OF NOVICES IN ORGANIZING ACTIVITIES TO STRENGTHEN THE NETWORK AND REDUCE RISK FACTORS ACCORDING TO BUDDHISM IN SAMUTSONGKHRAM PROVINCE
Keywords:
Novice Network, Activity, Risk Factor Reduction Network, Buddhism, Liquor and CigarettesAbstract
The purpose of this research article was to develop a network of novices in organizing activities to strengthen the network and reduce risk factors according to Buddhism in Samut Songkhram Province. It was an action research with 4 steps: 1. Surveyed the network participating in the activity. 2. Organized novice development activities. 3. Expanded the results of the activity. 4. Developed a prototype. The target group consisted of 20 youths in Samut Songkhram province, and interviews were conducted with 18 key informants. The tools used in the research included Research interview forms, evaluation forms before and after training, and focus group discussions. Data were collected by organizing novice ordination activities for 30 days. Data were analyzed descriptively, including tables and descriptions to describe events related to basic knowledge information.
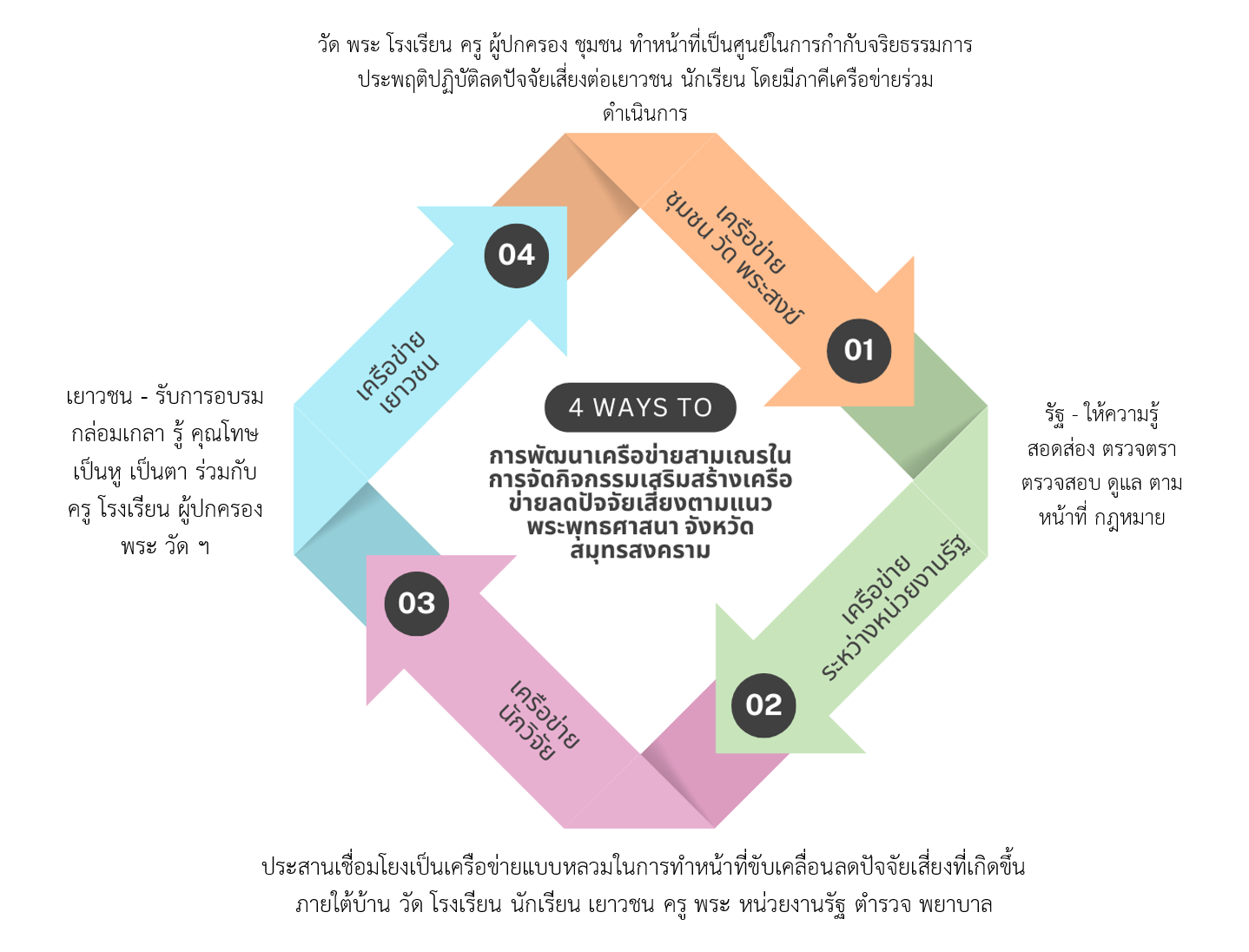
The research found that: 1. The network for developing novices consisted of houses, temples, and "Bowon" schools. 2. Organizing ordination activities for novices aimed to develop the students who participated in the project according to the framework of religion, social ethics, and responsibility. This created learning consistent with age and used the image of being ordained as a communication channel. It brought the image of a novice with students into public communication to achieve management of "Reducing risk factors" holistically. 3. Expanding the results of organizing activities for the community emphasized community participation, such as home visiting activities and activities to help older people. 4. Wat Indaram implemented policies and activities to develop youth and support the community. They organized a lunch program and provided educational scholarships for those ordained as novice monks. They also had risk reduction programs, which were psychological methods that created motivation and led to concrete practices. Additionally, the temple funded schools to teach Dharma studies under the policy of "Giving Dharma, Giving Funds." They organized novice monk ordination and temporary ordination activities during the summer break and held Buddhist youth camps annually. The impact on the community was assisting with necessities for the people.
References
พระครูปริยัติสาทร. (2019). กระบวนการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมการสูบบุหรี่ของพระสงฆ์สู่การเป็นต้นแบบปลอดบุหรี่ จังหวัดเลย. วารสารสถาบันวิจัยญาณสังวร, 10(2), 12–24.
พระครูพินิตปริยัติกิจ (สมบัติ วรธมฺโม) และคณะ. (2018). รูปแบบการมีส่วนร่วมของพระสงฆ์ในการแก้ไขปัญหาการติดยาเสพติด ในเขตปกครองคณะสงฆ์ภาค 2. วารสาร มจร สังคมศาสตร์ปริทรรศน์, 7(3), 1–14.
พระมหายุทธนา นรเชฏโฐ (ศิริวรรณ) และจุฑารัตน์ ทองอินจันทร์. (2018). แนวคิด ตัวชี้วัด องค์ประกอบบทเรียน และบูรณาการตามโครงการหมู่บ้านรักษาศีล 5. วารสารชุมชนวิจัย, 12(2), 204–214.
พระอุดมสิทธินายก (กำพล คุณงฺกโร) และพระมหานิกร ฐานุตฺตโร. (2019). การมีส่วนร่วมของพระสงฆ์ในการเสริมสร้างสุขภาวะและเครือข่ายทางสังคม เพื่อลดเหล้าบุหรี่เชิงพุทธบูรณาการในจังหวัดนนทบุรี. วารสาร มจร สังคมศาสตร์ปริทรรศน์, 8(4), 1–16.
วณิฎา ศิริวรสกุล และวัชรินทร์ อินทพรหม. (2018). รูปแบบการขับเคลื่อนนโยบายหมู่บ้านรักษาศีล 5 ให้ประสบความสำเร็จ. วารสารวิชาการ มหาวิทยาลัยธนบุรี, 12(29), 203–209.
สมคิด พุ่มทุเรียน และคณะ. (2019). วิเคราะห์กิจกรรมเชิงพุทธตามโครงการหมู่บ้านรักษาศีล 5 กับการหนุนเนื่องคุณค่านิยม 12 ประการ. วารสารบัณฑิตปริทรรศน์ วิทยาลัยสงฆ์นครสวรรค์, 7(1), 225–238.
Brown, L. M., & Green, T. W. (2022). Monastic education and community health initiatives: A qualitative study. International Journal of Health Services, 52(1), 99-114.
Chan, C. L., & Wong, M. T. (2018). A study on the effectiveness of Buddhist teachings in reducing drug abuse. Asian Journal of Counselling, 25(1), 34-47.
Lee, J. K., & Cheng, H. W. (2020). Role of Buddhist practices in curbing substance abuse among youth. Journal of Asian Studies, 79(3), 713-735.
Miller, D. S., & Thomas, G. A. (2019). Monks and substance abuse prevention: Insights from Southeast Asia. Substance Use & Misuse, 54(2), 248-256.
Smith, J. D., & Johnson, K. P. (2021). Buddhist principles in substance abuse prevention: A case study from Thailand. Journal of Religious and Health, 60(4), 2917-2931.