The Investigation of First-year University CFL learners’ Phonological Beliefs, Self-regulated Online Learning, and Online Learning Satisfaction: A Case Study of Mae Fah Luang University, Thailand
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
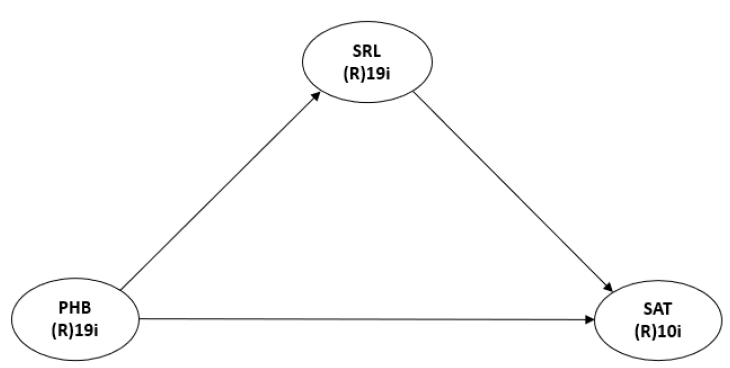
In a blended learning environment, this study aimed to investigate the relationship among Mae Fah Luang University first-year CFL learners' phonological beliefs, self-regulated online learning, and online learning satisfaction in Thai context. This research is quantitative research, the researcher applied the descriptive analysis to interpret the data results, while path analysis applied to examine the relationships. The findings emphasize the importance of addressing learners' phonological beliefs and highlight the value of pronunciation instruction in blended CFL courses. By integrating pronunciation-focused activities and fostering positive beliefs, instructors can enhance learners' engagement and overall satisfaction. Secondly, the study underscores the need to promote self-regulated learning skills among CFL learners. Providing explicit instruction on goal setting, time management, and metacognitive strategies can empower learners’ autonomy. Additionally, the identification of preferred pronunciation learning strategies and the significance of time management skills contribute to the design of effective blended CFL courses. The relevant pedagogical implications are also discussed. First, teachers are encouraged to raise students’ phonological awareness and help them realize the importance of Chinese pronunciation. Appropriated learner beliefs are crucial for sustaining motivated foreign language learning. Second, to enhance learners’ experience in a blended learning environment, instructors may consider effective instructional methods, such as explicit explanation of Chinese pronunciation, providing timely feedback and employing situation dialogues to improve learners’ speaking skills. Third, the instructors may design online learning activities to promote learners’ using cognitive learning strategies, and foster self-regulated learning skills. Fourth, instructors may create a supportive and non-judgmental learning environment to encourage learners to address their learning difficulties and seek help. Lastly, the research revealed the significance of time management skills in blended CFL learning. This emphasizes the importance of providing learners with resources and strategies to improve their learning autonomy, leading to more positive learning experiences.