Developing and Implementing a Smart Greenhouse for AI Education: Effects on High School Students’ Attitudes toward Artificial Intelligence
Main Article Content
Abstract
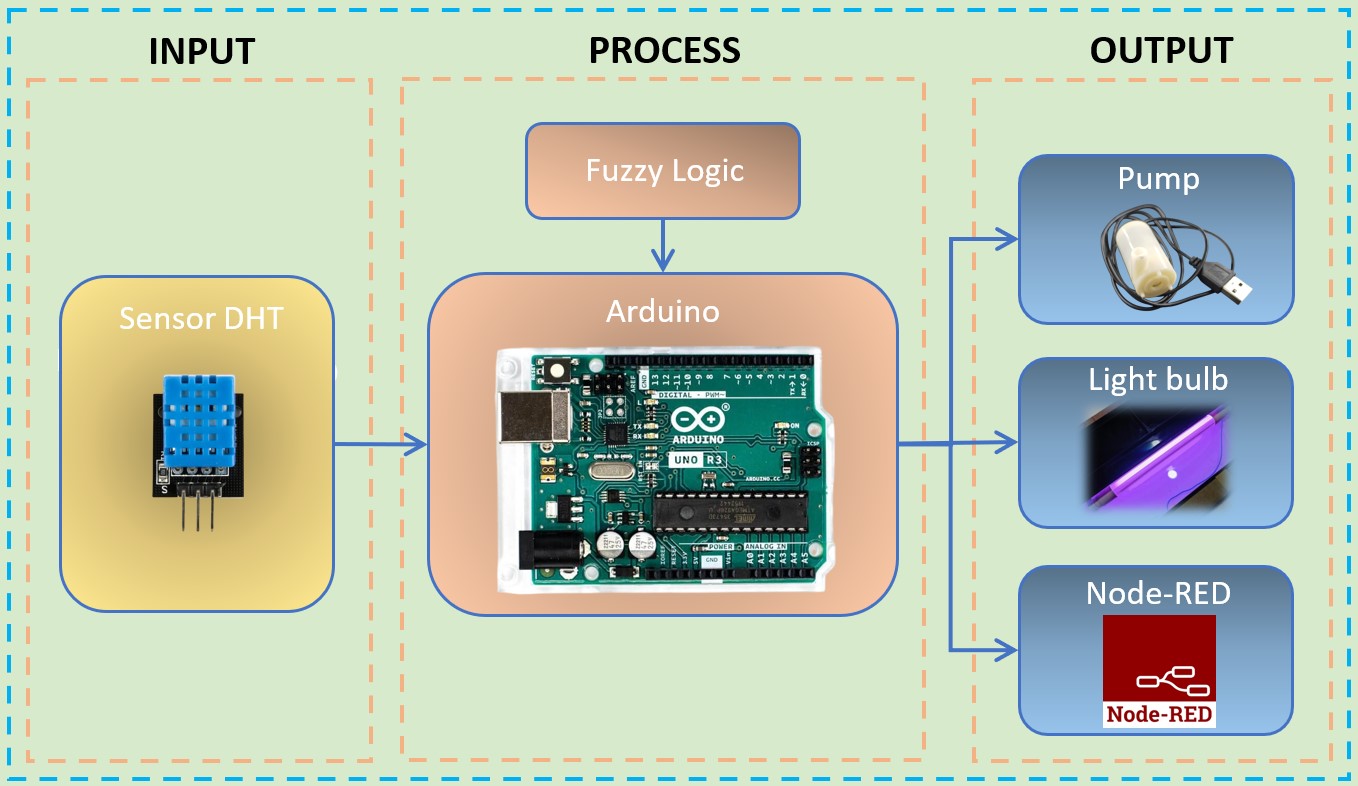
The integration of smart greenhouse technology into educational contexts offers an opportunity to enhance students’ understanding of artificial intelligence (Al) and its applications. This study investigates the on students’ attitudes toward AI technology. The smart greenhouse system utilizes microcontrollers, sensors, and Fuzzy Logic algorithms to and control environmental factors, particularly water and lighting systems, based on temperature detection through sensors. The system includes real-time data visualization via the Node-RED dashboard, enabling students to analyze and interpret the collected data effectively. This research was conducted with high school students who participated in project-based learning (PBL) activities centered on the smart greenhouse system. Post-learning surveys were administered to evaluate students’ attitudes toward AI technology. The findings highlight the potential of incorporating smart greenhouse systems into educational settings to enhance AI literacy and inspire innovation among students. Furthermore, the study emphasizes the importance of hands-on learning experiences in fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are essential for future technological advancements. Additionally, the attitude assessment showed that 85.1% of students agreed or strongly agreed they understood DHT sensor principles, 88.8% acknowledged improved understanding of fuzzy logic, and 81.5% responded positively to using the Node-RED dashboard. The project also enhanced creativity (92.6%), problem-solving skills (85.2%), and technological proficiency (96.3%).